Constellation of Models
Welcome to the forefront of artificial intelligence innovation, where we introduce the groundbreaking Constellation of Models (CoM) approach.
Learn MoreAbout CoM
The Constellation of Models (CoM) approach is a novel strategy designed to tackle complex, multi-modal tasks with unprecedented efficiency and precision. This framework provides organizations with a structured way to leverage multiple specialized AI models working in harmony.
Core Principles of the Constellation of Models
How the Dynamic Router Works
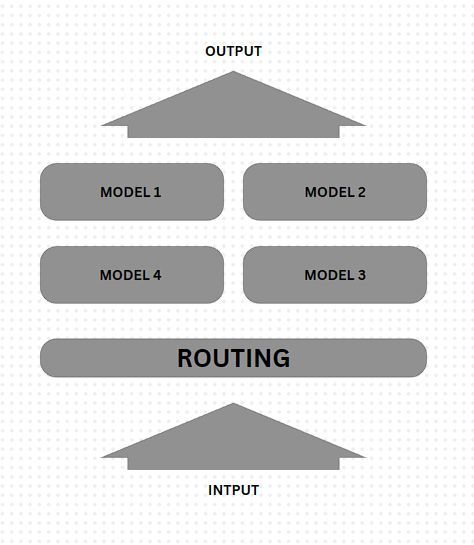
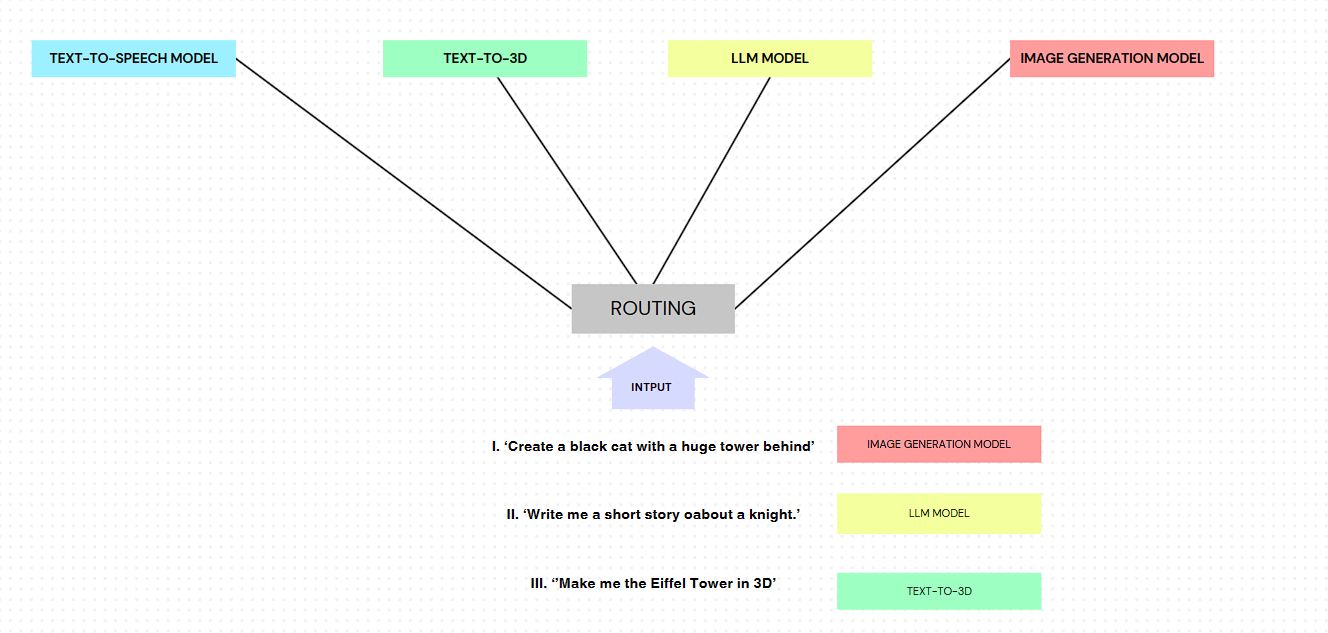
The CoM system revolves around a dynamic router that intelligently distributes tasks to a constellation of specialized, pre-trained models. Each model is an expert in its specific domain, enabling the system to handle a wide range of tasks with exceptional proficiency. In the landscape of multi-model strategies, the CoM approach stands out as a flexible and specialized solution. By establishing a standard based on this approach, we ensure consistency and efficiency in scenarios where multiple models must collaborate.
The CoM standard requires a dynamic router as a skilled orchestrator. This router ensures that each query is directed to the most capable model, optimizing overall system performance and resource utilization. By embracing the CoM approach as a standard, we move beyond the generalized methods of traditional models. This framework allows us to capitalize on the unique strengths of each component in our constellation, creating a system that exceeds the capabilities of its individual parts.
The CoM approach emerged from the need to address increasingly complex AI tasks that single models struggle with. Unlike traditional methods that rely on one large, generalist model, CoM harnesses the power of specialization and collaboration.
Advantages of CoM:
- Increased efficiency: Each model focuses on what it does best
- Improved accuracy: Specialized models often outperform generalist models in their domain
- Scalability: New models can be easily added to the constellation as needed
- Flexibility: The system can handle a wide variety of tasks without retraining
For example, in a complex task like autonomous driving, CoM might use separate models for object detection, path planning, and decision making, each optimized for its specific role.
Importance of Standardized Nomenclature
The router nomenclature presented in this table offers a clear and coherent naming convention for a broad spectrum of artificial intelligence models and tasks. This naming system is specifically designed to enable efficient model selection and routing in multi-model AI systems, such as those utilizing the Constellation of Models (CoM) approach.
The nomenclature follows a simple pattern, starting router names with the prefix "CoM_" (signifying Constellation of Models) followed by a concise descriptor of the model's function or task. For instance, "CoM_ImageClassification" denotes a router dedicated to image classification tasks, while "CoM_Text2Image" signifies a router for text-to-image generation models.
Encompassing a wide variety of AI tasks, this naming convention includes computer vision, natural language processing, audio processing, and reinforcement learning. By establishing a standardized naming system, this nomenclature enhances interoperability and streamlines the development of AI systems that leverage multiple specialized models.
The dynamic router is the brain of the CoM system. It analyzes incoming tasks and determines the best model or sequence of models to handle them. This decision is based on factors such as:
- The nature of the input data (text, image, audio, etc.)
- The specific requirements of the task
- The performance history of each model
- The current load on each model
For instance, in a customer service application, the router might direct general inquiries to a text-based chatbot, route voice calls to a speech recognition model followed by a natural language processing model, and escalate complex issues to a human operator.
| Router Name | Description |
|---|---|
| CoM_Small_A | Audio |
| CoM_I | Image |
| CoM_L | LLM (Large Language Model) |
| CoM_AI | Audio and Image |
| CoM_AL | Audio and LLM |
| CoM_IL | Image and LLM |
| CoM_AIL | Audio, Image, and LLM |
| CoM_T2TA | Text-to-Text and Audio |
Distributed AI Models Across Multiple Servers: A New Frontier
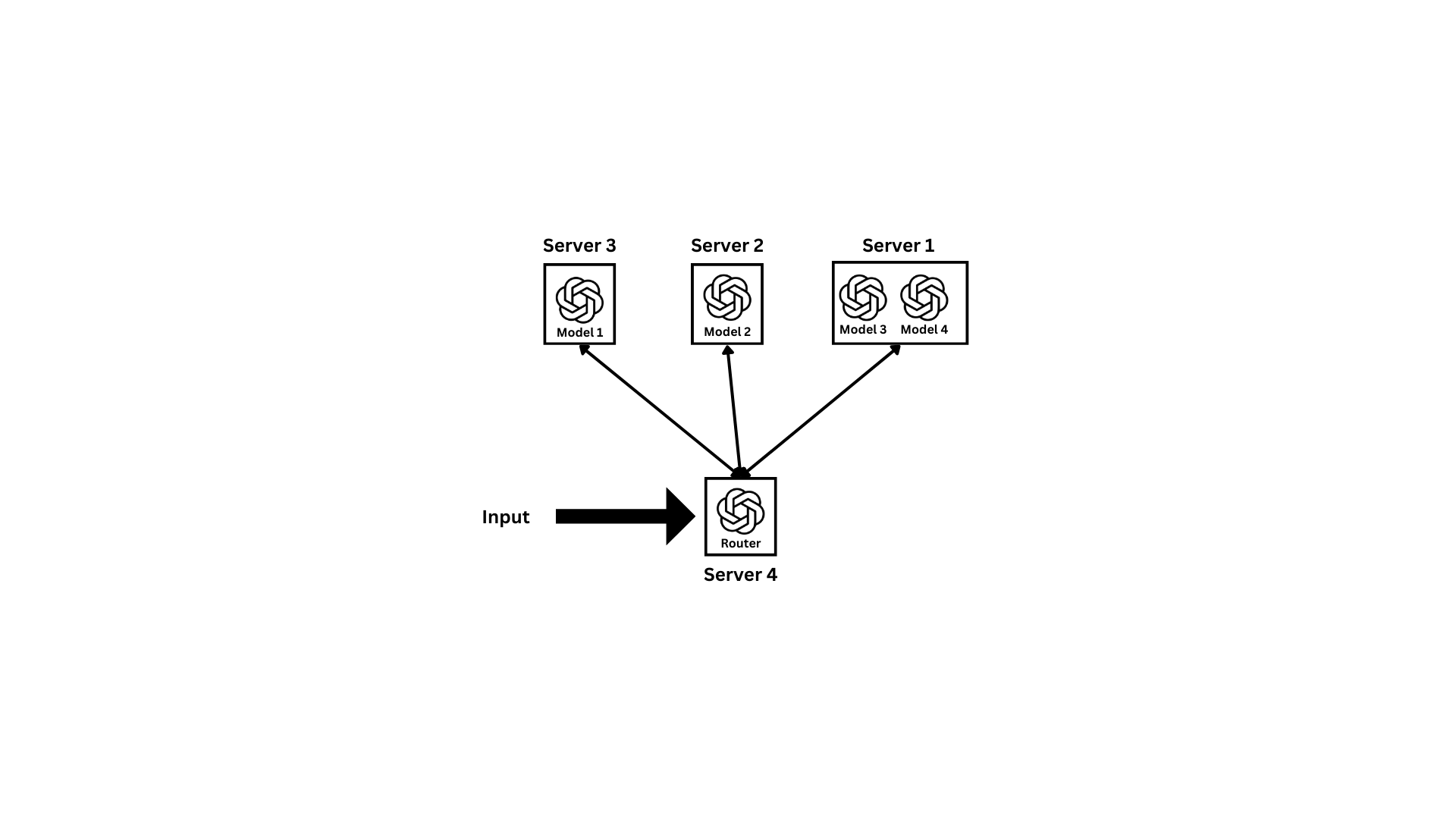
Imagine a world where artificial intelligence models are no longer confined to a single server but are instead distributed across multiple servers, each harnessing unique computational power and specialized capabilities. This is not just a distant vision but a rapidly approaching reality that promises to revolutionize how we develop and deploy AI systems.
Unlocking Potential with Distributed Architecture
By distributing models across different servers, we unlock unprecedented potential for scalability, efficiency, and performance. Each server can be tailored to the specific needs of the models it hosts, ensuring optimal computational environments and minimizing resource waste.
Moreover, this distributed architecture allows for seamless integration of new models and servers, enabling AI systems to adapt and grow with ever-evolving requirements and challenges.
The Constellation of Models Approach: Embracing Multi-Server Architecture
The Constellation of Models (CoM) approach exemplifies this paradigm shift. By dynamically routing tasks to specialized models hosted on different servers, CoM enables AI systems to tackle complex, multi-modal tasks with unparalleled flexibility and expertise.
This innovative strategy not only enhances the overall performance of AI systems but also paves the way for more diverse and sophisticated applications.
Shaping the Future of AI with Distributed Models and Servers
Embracing a distributed, multi-server architecture for AI models opens up a world of possibilities. As we continue to push the boundaries of artificial intelligence, it is essential to recognize and capitalize on the potential of distributed models and servers to drive innovation and shape the future of AI.
Protecting AI Models with Firewall at the Prompt Level: Enhancing Security and Preventing Injection Attacks
As artificial intelligence systems become more sophisticated and distributed across multiple servers, ensuring the security and integrity of AI models becomes a paramount concern.
The Importance of Firewall Protection at the Prompt Level
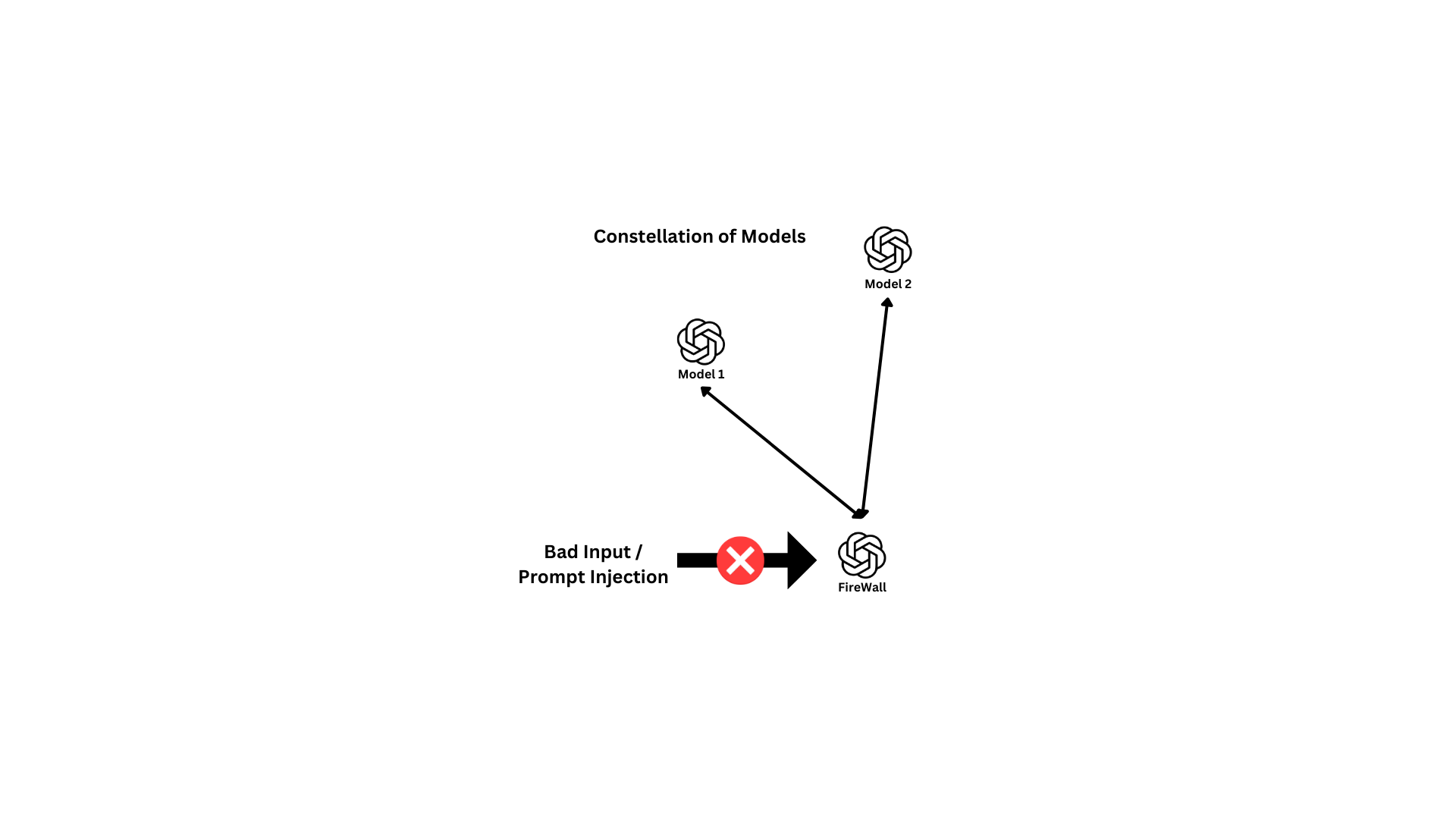
Implementing a firewall at the prompt level is a crucial measure to protect AI models from potential threats, such as injection attacks that could target vulnerabilities in a server's default configuration.
A firewall at the prompt level acts as a barrier, filtering and monitoring incoming requests to the AI models, ensuring that only legitimate and safe queries are processed.
Safeguarding AI Systems with Robust Security Measures
By integrating a firewall at the prompt level, AI systems can effectively mitigate the risk of unauthorized access, data manipulation, and other malicious activities that could compromise the performance and reliability of the models.
This security measure complements the Constellation of Models (CoM) approach, ensuring that the distributed architecture benefits from protection tailored to each model's unique requirements and threat landscape.
Building Trust and Resilience in AI through Enhanced Security
As we continue to push the boundaries of artificial intelligence, prioritizing security at every level of the AI system is essential. By implementing a firewall at the prompt level, we can build trust and resilience in AI, safeguarding the future of intelligent systems against evolving threats.
Specific Threats Countered by Prompt-Level Firewalls
As AI models become increasingly important in organizations, their significance will parallel that of well-configured networks. Just as robust network infrastructure is vital for operations and communication, an efficient AI model infrastructure will be indispensable for processing, analyzing, and making intelligent decisions based on vast amounts of data.
With the growing number of models, data flows and interactions between them will become too complex for human oversight. This complexity necessitates implementing intelligent management systems like the CoM approach, which can dynamically orchestrate tasks and data among models, ensuring optimal performance and resource allocation.
Moreover, the proliferation of AI models presents new security concerns, such as vulnerabilities and hallucinations. Models can inadvertently expose sensitive information or generate incorrect outputs, leading to potential risks and misguided decisions. To mitigate these risks, establishing a framework that monitors, secures, and validates the behavior of each model within the CoM ecosystem is essential, ensuring the integrity and reliability of the overall system.
- Injection attacks: Filtering out malicious code or commands embedded in prompts
- Data poisoning: Detecting and blocking attempts to introduce biased or harmful training data
- Model probing: Preventing attempts to extract sensitive information from the model
Integration with Broader AI Security Strategy
Prompt-level firewalls are part of a comprehensive security approach that also includes:
- Robust authentication and authorization mechanisms
- Continuous monitoring and auditing of model inputs and outputs
- Regular security assessments and penetration testing
While these measures enhance security, they may introduce slight latency. However, the trade-off is generally worthwhile for maintaining the integrity and reliability of AI systems.
The Growing Importance and Challenges of Managing Multiple Models
AI Models: The New Organizational Backbone
As the adoption of AI models continues to grow, their significance is becoming analogous to the advent and criticality of a well-configured network within an organization. Just as a robust network infrastructure is vital for smooth operations and communication, an efficient AI model infrastructure will be indispensable for:
- Processing vast amounts of data
- Analyzing complex information
- Making intelligent decisions in real-time
Complexity Demands Intelligent Management
With an ever-increasing number of models, the data flows and interactions between them are becoming too complex for human oversight. This complexity necessitates the implementation of intelligent management systems like the CoM approach, which can:
- Dynamically orchestrate tasks among models
- Efficiently allocate resources
- Ensure optimal performance across the AI ecosystem
New Security Concerns and Challenges
The proliferation of AI models presents new security concerns and challenges, including:
- Vulnerabilities to external attacks
- Potential for model hallucinations
- Inadvertent exposure of sensitive information
- Generation of incorrect or biased outputs
These issues can lead to potential risks and misguided decisions, emphasizing the need for robust security measures.
Mitigating Risks with a Comprehensive Framework
To address these challenges, it is essential to establish a framework that:
- Monitors the behavior of each model within the CoM ecosystem
- Implements rigorous security protocols
- Validates model outputs for accuracy and reliability
- Ensures the integrity of the overall system
By implementing such a framework, organizations can harness the power of multiple AI models while minimizing associated risks and maintaining system reliability.
AI Model Types and Their Security Vulnerabilities
| Model Type | Importance | Security Vulnerabilities | Examples and Best Practices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Computer Vision | Image and video analysis, object detection, autonomous systems | Adversarial attacks, Data privacy leakage |
Example: Subtle modifications to stop sign images to confuse autonomous vehicles. Best Practices: Implement adversarial training, use ensemble models, regularly update with diverse data. |
| Natural Language Processing | Text analysis, sentiment classification, machine translation, chatbots | Adversarial inputs, Data privacy leakage, Hallucinations |
Example: Injecting misleading phrases to manipulate chatbot responses. Best Practices: Use robust tokenization, implement content filtering, regular model evaluations. |
| Audio Processing | Speech recognition, speaker identification, audio synthesis | Adversarial audio attacks, Unauthorized access |
Example: Using synthesized voice commands to access secure systems. Best Practices: Implement multi-factor authentication, use noise reduction techniques, continuous model updating. |
| Reinforcement Learning | Optimization, decision-making, autonomous agents, robotics | Reward hacking, Exploitation of environment |
Example: Manipulating the reward function to encourage unintended behaviors in game AI. Best Practices: Implement robust reward modeling, use constrained optimization, extensive testing in varied environments. |
| Tabular Data Processing | Structured data analysis, prediction, and classification | Data privacy leakage, Model inversion attacks |
Example: Inferring sensitive individual data from aggregated model outputs. Best Practices: Apply differential privacy techniques, use secure multi-party computation, limit model output precision. |